ABOUT US
Virtual Reality Centre
The Virtual Reality Centre (VRC) of the Centre for Teaching and Learning, HSUHK, aims to support teaching and learning activities through extended reality technologies. The centre is equipped with Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE)-based interactive and immersive virtual reality system in its Virtual Reality and Big Data Analytics Laboratory (VRBD Lab). The centre applies virtual reality and augmented reality technologies and big data visualisation and analysis to various disciplines through the virtual reality systems and simulation tools.. The VR system has been developed to provide vivid stereoscopic views of sceneries in 3D design to facilitate visualization on 3D illustration of industrial supply chain operations, geometrical theories, financial modelling, and healthcare logistics operations. The system provides a versatile and powerful interactive virtual reality platform for operators to train and practice in complex and critical operations before assigned to work in real life operations. With the support of CAVE system and simulation software in the center, sophisticated big data in multi-dimension analysis will be carried out. The center aims to focus on the interactive visualization and big data analytics research and development in the areas of supply chain and logistics, banking and finance, business analytics, healthcare logistics, and heritage as well as provide an excellent interactive 3D learning platform to the students, academic researchers, and industrial practitioners.
Centre Members and Staff
Director: Ir Dr Eugene WONG
Senior Systems Engineer: Mr Matt CHAN

About Project
The increased complexity in data and operation processes in global organisations has posted a growing demand for big data and process analysis in most of the industries, especially in logistics and transportation, supply chain finance and healthcare logistics. The current mode of classroom teaching and learning with the help of textbooks and case studies, field studies and on-site visits, are not able to demonstrate the complexity of operations to students. Very often graduates, even practitioners, are not able to visualize the end-to-end process of the entire supply chain, finance, or medical operations. The government of Hong Kong is recently promoting the use of virtual learning initiatives to support education needs. To achieve the development of an interactive virtual reality platform for learning and big data analytics, a Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE) system is much needed in setting up various modules for a number of degree programs in the School. This project aims to develop a cost-effective, fully immersive and interactive visualization CAVE system that provides extremely vivid stereoscopic views of sceneries in 3D design. The CAVE will be applied in teaching, learning and research. The operations of air cargo terminal operations will be first developed in the project.
Acknowledgement: The project work was partially supported by Quality Enhancement Support Scheme (QESS) grant from the Education Bureau of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China (Project No.: 05/QESS/2015).
About The Hang Seng University of Hong Kong
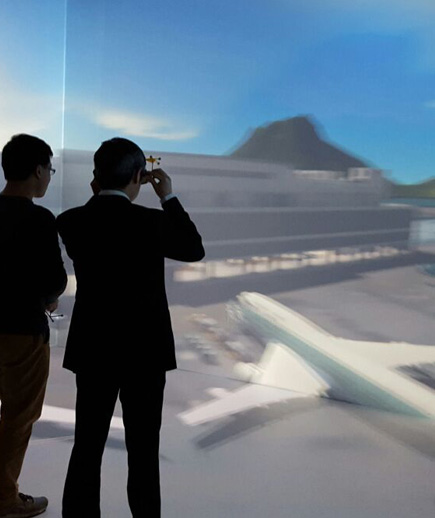

VIRTUAL REALITY
VIRTUAL REALITYThe concept of virtual reality is first introduced by Ivan Sutherland in 1963. He invented The Ultimate Display in 1965 to integrate the design, construction, navigation and habitation of virtual world into the computer. In recent decades, the definition of virtual reality is focused on the key elements of immersion, interaction, dynamic control, and human-computer interface. In 1990s, virtual reality is defined as an immersive and interactive experience generated by computer. Brooks in 1999 defined a virtual reality experience as any in which the user is effectively immersed in a responsive virtual world with a dynamic control point of view. Virtual reality is also defined as the sense of being in an environment, generated by natural or mediated means, through technological hardware and dimensions. In 2000s, virtual reality is interpreted as a closed computer system that consists of a virtual environment as well as a software and hardware interface, which allows interaction between a human and a computer. Later virtual reality is termed by using four key elements: a virtual world, immersion, sensory feedback and interactivity. In the 2010s, Dioni and Gilbert described virtual reality as computer-generated simulations of three-dimensional objects or environments with seemingly real, direct, or physical user interaction. Recently, virtual reality is referred to a collection of technologies for generating a human-computer interface that allows people to interact efficiently with, become immersed in, and to feel the presence in computerized 3D environments, while using their natural senses and motor skills in real time.
Big Data
Big data analytics is the process of collecting, examining and analysing large data sets to uncover hidden patterns, unknown correlations, market trends, customer preferences and other useful business information. The data sets are usually large and complex that traditional data processing applications are inadequate. Challenges include analysis, capture, data curation, search, sharing, storage, transfer, visualization, querying, updating and information privacy. The big data analytical findings can lead to more effective marketing, new revenue opportunities, better customer service, improved operational efficiency, competitive advantages over rival organizations and other business benefits.





